How to Treat Chickenpox in Children?
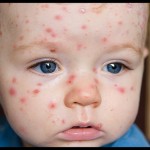 Chickenpox is a childhood skin related disease which is caused by viral infection. Though at one time it would spread like an epidemic at various places, but due to advancement of preventive medicines and general awareness of masses, the incidence of chicken pox have reduced considerably especially in the developed societies all around the world.
Chickenpox is a childhood skin related disease which is caused by viral infection. Though at one time it would spread like an epidemic at various places, but due to advancement of preventive medicines and general awareness of masses, the incidence of chicken pox have reduced considerably especially in the developed societies all around the world.
Vaccinations of the children at specific ages and universal vaccination programmes have resulted in reduction of incidents of chicken pox to a great extent. However, in countries or the societies where proper preventive vaccination programmes are not followed, chicken pox does appear. This is also a fact that in some cases where vaccination has been done the child does get affected, but this is rare. It is said that this disease happens only once in the life time of a person. Children between the age of 5 and 9 are most likely to contract chickenpox but children up to the age of 15 should take maximum care. Winter and spring time is the season when this disease affects the most.
The first dose of the preventive vaccine is administered to the child between the ages of 12 to 15 months. A booster dose is given when the child is between the ages of 4 to 6 years. It is recommended that the people above the age of 15 who have never contracted chickenpox should also get vaccinated twice with a gap of 28 days between two doses.
Chickenpox is a highly contagious disease. It spreads from child to child by contact or the particles get airborne and enter the respiratory system of the children. The fluid from the blisters or sores gets into the atmosphere and spreads, affecting other kids. The disease also gets transmitted through contact with the sick person or his clothes or if the discharge of water used for washing is in open drains. The maximum chances of the disease being contagious are for the first five days, i.e. from the day the rash appears to next five days. When the sores get crusted the chances of spreading of the disease gets reduced.
Symptoms and first signs start to appear between 10 to 21 days after the kids contact the virus. The child gets fever which could be up to 102°F, feels weakness and rashes starts to appear on the body, giving first indication of appearance of disease. In rare cases, the patient may have no rashes. The rash develops into red spots which get converted to blisters which have burning sensation. Before the crusts start to develop the blisters convert to open sores. The process of appearance of rash and spots starts from the scalp and travels towards the trunk, arms and legs. The rash is very itchy and painful.
Treatment of chickenpox can be done by various ways. Some of the commonly used methods are:
- Soothing bath helps relieve itching and gives much needed relief to the patient. Adding fully grounded oatmeal to the bath can have soothing effect. About two cups of finely grounded oatmeal can be added to the bath tub. Similarly a cup of baking soda can also be added to reduce the itching effect.
- Calamine lotion, readily available as an over the counter lotion in all stores, is most commonly used and recommended by doctors. This, when applied on the blisters, helps to dry them and smoothen the skin.
- To reduce severe itching, antihistamine, an over the counter drug is of great help. This drug causes drowsiness and helps the patient to have good sleep. However certain versions of this drug are available which helps reduce itching without causing drowsiness.
- Though there is a great urge to scratch but it will be better to avoid scratching. Scratching may result in increase in chances of development of secondary bacterial infection.
- Certain anti bacterial medicines are prescribed by the doctors to control bacterial infection and reduce the time period, severity and instances of fever. In milder cases without other complication, recommended dose of these medicines can be taken, these are quite effective.